
AMD vs Intel Title Fight! – XMG Core 15 Red vs Blue Comparison
Check on YouTube
With two of the same laptops with the XMG Core 15 giving absolutely equal treatment to both machines and everything else being the same, which is better between Intel and AMD?
Specs:
Same RTX 3060 GPU.
Same 62Wh battery.
Same 1920 by 1080, 165 Hz, IPS display.
We run an Apples to Apple comparisons between Intel and AMD CPUs using Core i7-11800H Intel inside laptop costing $2,188 and AMDs Ryzen 7 5800H.
The AMD also has 8 cores and 16 threads and boosts just 0.2GHz lower and ends up priced almost $100 below its Intel competition.
Exterior:
Same chassis.
Same port arrangement.
The IO is not exactly the same.

USB-C can be used as a single cable docking solution, running your display, network and peripherals and power.
Thunderbolt does it better wit more bandwidth for displays and storage, daisy chain support and compatibility with pesky Thunderbolt only peripherals.
Performance:
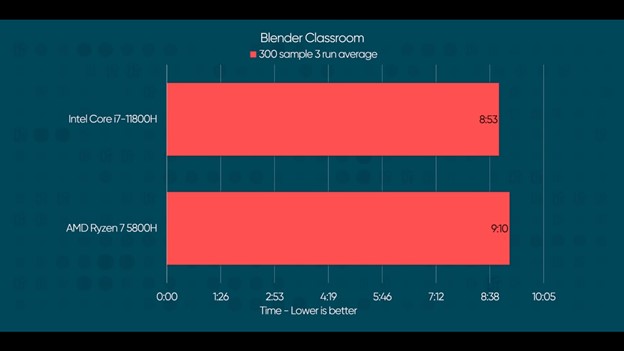
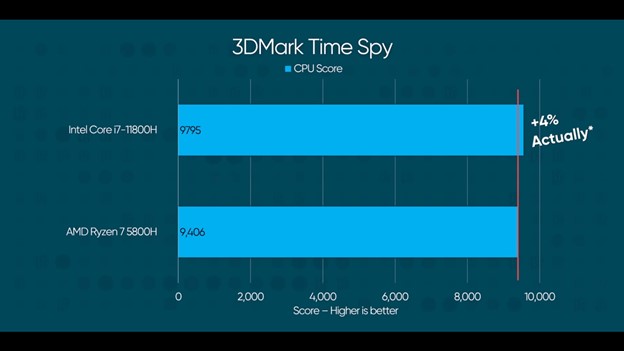
Surprisingly Intel is the winner in these two tests with Blender-Classroom between 8 and 30 seconds of improvement on repeat tests and 3DMark reporting a 4.1% CPU score improvement.
Gaming:
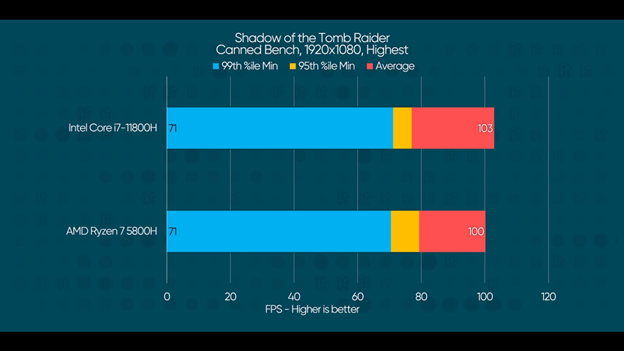
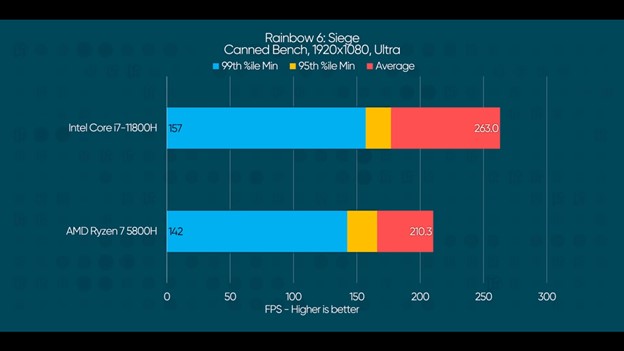
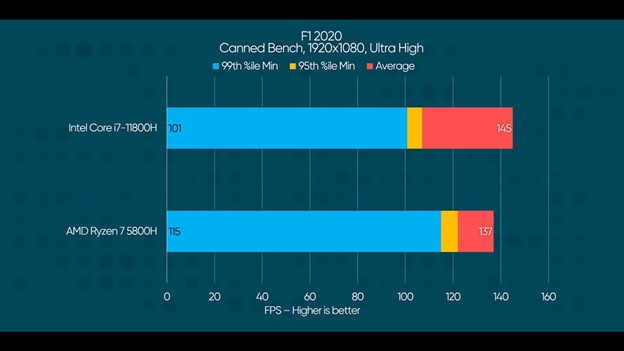
Here the 11800H shows a mild lead across the board with up to 15% improvement over AMD.
Power:
In spite of both CPUs having default TPDs of 45W, The Ryzen CPU settled down at around 60W with the Intel chip self-supporting power consumption as high as 100W and settling in around 80W.
On the desktop, 20W is like having more RGB in your case, but on mobile, PCMark’s Modern Office battery test gave AMD a 31% edge over Intel at the same screen brightness.
Read and Write:
The Core i7-11800H has support for PCIe Gen 4 WHICH GIVES MANUFACTURERS AN OPORTUNITY TO nearly double the sequential read and write performance of the system drive for just the $60 DIFFERENCE BETWEEN a Samsung 980 Pro and the 970 EVO Plus that XPG paired with AMDs Ryzen 7 5800H.
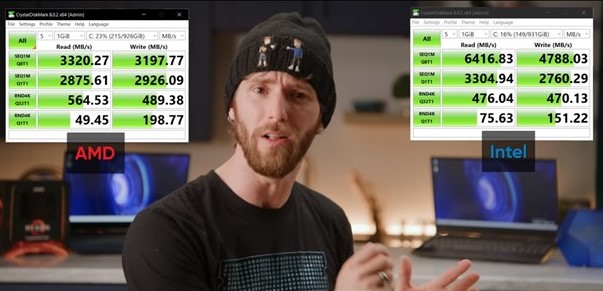
Storage:
In PCMark’s storage test, the gap begins to narrow.
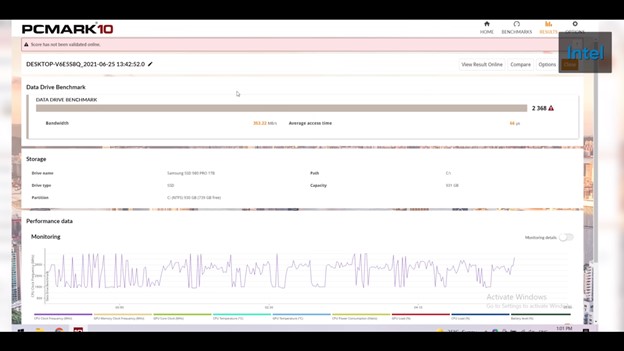
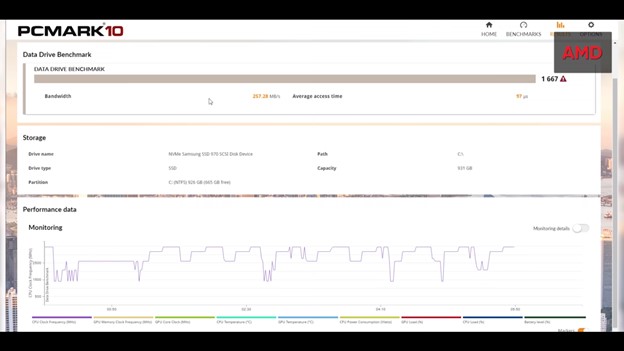
GPU:
The PCIe advantage extends past the storage to the GPU. While the GeForce RTX 3060’s are capable of running PCIe Gen 4 with up to 16 lanes which the Intel system is fully utilizing thanks to the additional 4 PCIe lanes,
The AMD is just connected to a quarter of that speed with only 8 Gen 3 lanes.
Conclusion:
The Intel machine wins on performance
The AMD wins on battery life.




This Post Has 0 Comments